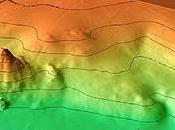
Prior to 1980, Mount St. Helens formed a conical, youthful volcano sometimes known as the Fuji-san of America. During the 1980 eruption the upper 400 m of the summit was removed by slope failure, leaving a 2 x 3.5 km horseshoe-shaped crater now partially filled by a lava dome. Mount St. Helens was formed during nine eruptive periods beginning about 40-50,000 years ago and has been the most active volcano in the Cascade Range during the Holocene. Prior to 2200 years ago, tephra, lava domes, and pyroclastic flows were erupted, forming the older St. Helens edifice, but few lava flows extended beyond the base of the volcano. The modern edifice was constructed during the last 2200 years, when the volcano produced basaltic as well as andesitic and dacitic products from summit and flank vents. Historical eruptions in the 19th century originated from the Goat Rocks area on the north flank, and were witnessed by early settlers.
(some text & images : Smithsonian Institution)


SRC Location UTC Date/time M D INFORMATION
USGS Mount St. Helens Area, Washington Mar 17 21:28 PM 2.5 1.1 MAP

SRC Location UTC Date/time M D INFORMATION
USGS Washington Mar 22 10:01 AM 2.7 5.9 MAP

SRC Location UTC Date/time M D INFORMATION
ER Mount Rainier, Washington (startup Record) Jan 01 00:00 AM 0.1 0.1 MAP
SHARE YOUR EARTHQUAKE EXPERIENCE WITH USSRC Location UTC Date/time M D INFORMATION
ER Glacier Peak, Washington (startup Record) Jan 01 00:00 AM 0.1 0.1 MAP
Enter Email (not compulsory)
Your current location
MMI II (Very weak shaking)
?
People :
Felt by persons at rest, on upper floors or favorably placed.
MMI III (Weak shaking)
?
People :
Felt indoors; hanging objects may swing, vibration similar to passing of light trucks, duration may be estimated, may not be recognized as an earthquake.
MMI IV (Light shaking)
?
People :
Generally noticed indoors but not outside. Light sleepers may be awakened. Vibration may be likened to the passing of heavy traffic, or to the jolt of a heavy object falling or striking the building.
Fittings :
Doors and windows rattle. Glassware and crockery rattle. Liquids in open vessels may be slightly disturbed. Standing motorcars may rock.
Structures :
Walls and frames of buildings, and partitions and suspended ceilings in commercial buildings, may be heard to creak.
MMI V (Moderate shaking)
?
People :
Generally felt outside, and by almost everyone indoors. Most sleepers awakened. A few people alarmed.
Fittings :
Small unstable objects are displaced or upset. Some glassware and crockery may be broken. Hanging pictures knock against the wall. Open doors may swing. Cupboard doors secured by magnetic catches may open. Pendulum clocks stop, start, or change rate.
Structures :
Some large display windows cracked. A few earthenware toilet fixtures cracked.
MMI VI (Strong shaking)
?
People
Felt by all. People and animals alarmed. Many run outside. Difficulty experienced in walking steadily.
Fittings :
Objects fall from shelves. Pictures fall from walls. Some furniture moved on smooth floors, some unsecured free-standing fireplaces moved. Glassware and crockery broken. Very unstable furniture overturned. Small church and school bells ring. Appliances move on bench or table tops. Filing cabinets or “easy glide” drawers may open (or shut).
Structures :
Slight damage to buildings with low standard. Some stucco or cement plaster falls. Large display windows broken. Damage to a few weak domestic chimneys, some may fall.
Environment :
Trees and bushes shake, or are heard to rustle. Loose material may be dislodged from sloping ground, e.g. existing slides, talus slopes, shingle slides.
MMI VII (Very strong shaking)
?
People
General alarm. Difficulty experienced in standing. Noticed by motorcar drivers who may stop.
Fittings :
Large bells ring. Furniture moves on smooth floors, may move on carpeted floors. Substantial damage to fragile contents of buildings.
Structures :
Unreinforced stone and brick walls cracked. Low standard buildings cracked with some minor masonry falls. A few instances of damage to buildings of ordinary workmanship. Unbraced parapets, unbraced brick gables, and architectural ornaments fall. Roofing tiles, especially ridge tiles may be dislodged. Many unreinforced domestic chimneys damaged, often falling from roof-line. Water tanks Type I burst. A few instances of damage to brick veneers and plaster or cement-based linings. Unrestrained water cylinders (hot-water cylinders) may move and leak. Some common windows cracked. Suspended ceilings damaged.
Environment :
Water made turbid by stirred up mud. Small slides such as falls of sand and gravel banks, and small rock-falls from steep slopes and cuttings. Instances of settlement of unconsolidated or wet, or weak soils. Some fine cracks appear in sloping ground. A few instances of liquefaction (i.e. small water and sand ejections).
MMI VIII (Severe shaking)
?
People
Alarm may approach panic. Steering of motorcars greatly affected.
Structures :
Low standard buildings heavily damaged, some collapse. ordinary workmanship buildings damaged, some with partial collapse. Reinforced masonry or concrete buildings damaged in some cases. A few instances of damage to buildings and bridges designed and built to resist earthquakes. Monuments and pre-1976 elevated tanks and factory stacks twisted or brought down. Some pre-1965 infill masonry panels damaged. A few post-1980 brick veneers damaged. Decayed timber piles of houses damaged. Houses not secured to foundations may move. Most unreinforced domestic chimneys damaged, some below roof-line, many brought down.
Environment :
Cracks appear on steep slopes and in wet ground. Small to moderate slides in roadside cuttings and unsupported excavations. Small water and sand ejections and localized lateral spreading adjacent to streams, canals, lakes, etc.
MMI IX (Violent shaking)
?
Structures
Many low standard buildings destroyed. Ordinary workmanship buildings heavily damaged, some collapse. Reinforced masonry or concrete buildings damaged, some with partial collapse. Buildings and bridges designed and built to resist earthquakes damaged in some cases, some with flexible frames seriously damaged. Damage or permanent distortion to some buildings and bridges, designed and built to normal use standards. Houses not secured to foundations shifted off. Brick veneers fall and expose frames.
Environment :
Cracking of ground conspicuous. Landsliding general on steep slopes. Liquefaction effects intensified and more widespread, with large lateral spreading and flow sliding adjacent to streams, canals, lakes, etc.
Write your experience and/or additional text here (max. 500 characters)